Methane Detection
The airborne solution for fast and high-precision methane detection from a distance
How it works
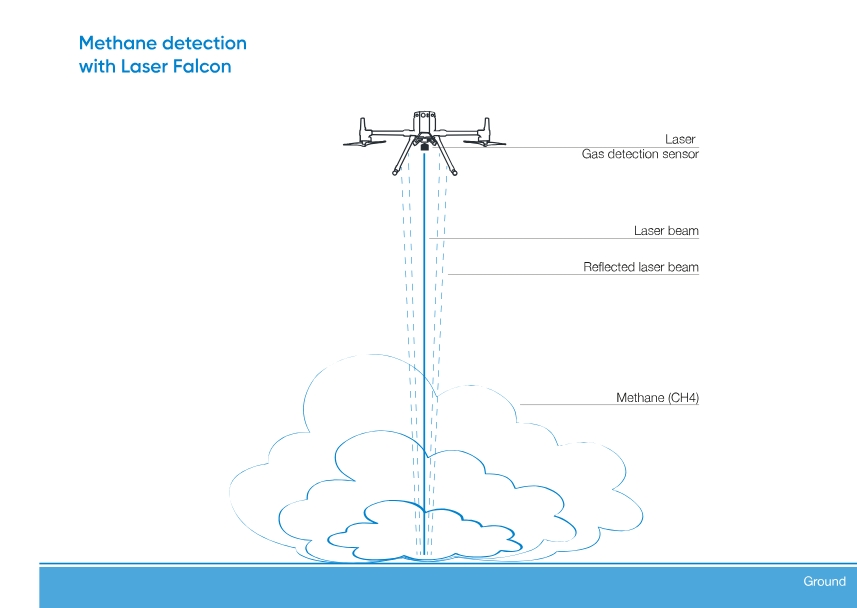
The Laser Falcon uses TDLAS-tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy. The methane detector emits the laser beam and measures the reflected energy. When the laser hits a methane cloud, energy is absorbed, and the sensor registers the presence of methane.
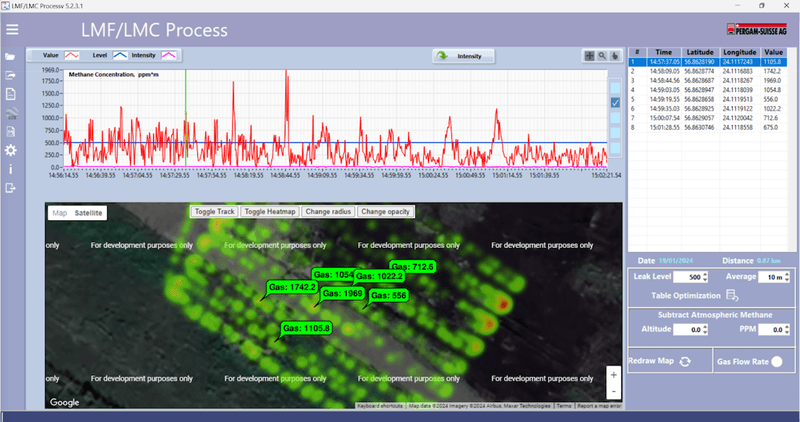
The Laser Falcon sensor is designed for airborne use and needs to be mounted on the UAV along with the SkyHub onboard computer. The SkyHub onboard computer records the sensor readings and GPS coordinates with high precision, making it possible to build accurate methane emission maps and develop precise work orders for field teams. Drones help significantly reduce the area for on-foot inspection and make it at least 3 times faster.
Benefits of methane inspection with UAV
Traditional methane leak detection methods involve using a car, helicopter, or ground crew with handheld devices. Sometimes, the use of these methods can be complicated, especially in the case of small, hazardous, or hard-to-reach areas. Using helicopters for surveying small areas is not economically feasible, and roads are needed for cars equipped with methane detection sensors. Ground inspections take a lot of time and are not always safe for humans due to hazardous areas. Installing stationary detectors at landfills is difficult because the active area of the landfill constantly changes the terrain.
-
The better approach is to fly a drone (UAV) to carry the methane sensor.
A drone is compact and easy to transport and deploy. It is also highly precise in following planned survey lines and can be used anywhere there is at least a small area for take-off and landing near the surveyed area.
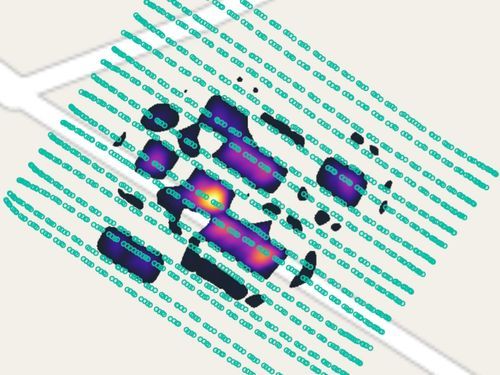
Consider mapping methane leaks on a landfill using, for example, a DJI M350. Given its battery endurance, speed of 3-7 m/s (recommended to Falcon sensor), line spacing of 5-15 meters, and elevation variations, it can cover roughly 2.5-5 hectares per battery set. That means the UAV can survey 5 hectares in just one hour, which is over 6 times faster than ground crews and 2 times faster than sniffer drones.
-

Works in a hazardous environment
With UAV, you can thoroughly survey landfills, a gas pipeline section, or other gas infrastructure facilities where access from the ground is impossible or restricted. The system works in a hazardous environment that humans cannot approach freely. A drone with Laser Falcon can detect methane molecules with high confidence at a distance of up to 30m.

Precise positioning
The drone's precise positioning while following the survey routes and ability to fly at a constant speed and specified altitudes result in high-accuracy and repeatable measurements.
-

Cost-efficient
For small survey areas, the mobilization cost for the helicopter or car with methane detection equipment may exceed the survey's price. A highly portable UAV system saves time for mobilization and deployment and will be more cost-efficient than a standard approach.
Typical applications
UAV-borne methane detection system allows fast remote scanning for leak detection and location. Discover the typical applications for drone-borne methane detection systems
-

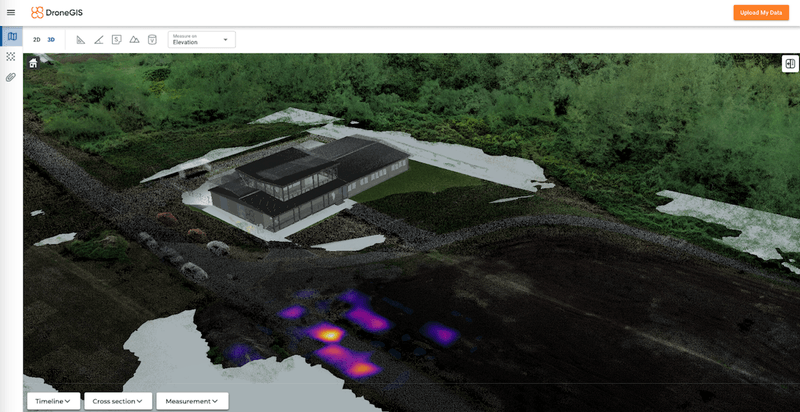
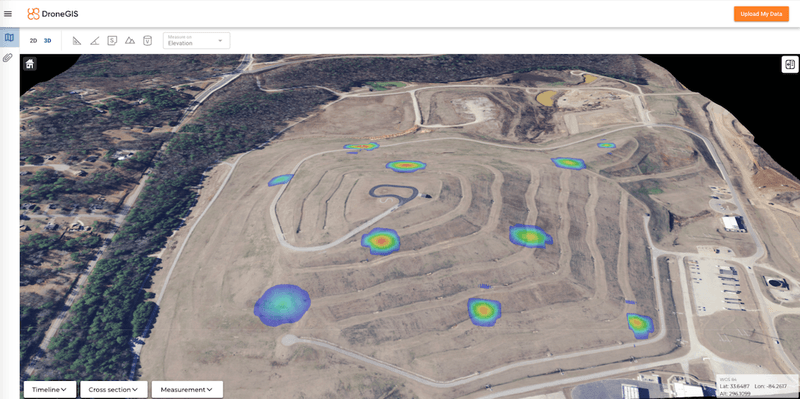
Landfills inspection
-

Gas pipeline inspection
-

Gas facilities inspection (gas tank, pressure station, etc.)

Case Studies
-

Methane Leak Detection with a Drone: Proof of Concept
-

Drone Technology enables three times faster Methane Emissions Monitoring in Landfills
-

Identifying Landfill Hotspots and Methane Emissions with Drones
-

Laser Falcon sensor used to detect methane leaks in the landfills in the Netherlands
-

Test & evaluation of the Falcon Methane sensor to assess the effectiveness of UAV emissions detection
Data Sets
The methane detection system records data in two standard formats
Discover the downloadable data-sets of drone based methane detection surveys by SPH Engineering »»»
Frequently Asked Questions
| Line spacing / Speed | 4 m/s | 5 m/s | 6 m/s | 7 m/s |
| 2m | 2.3 | 2.9 | 3.5 | 4 |
| 4m | 4.6 | 5.8 | 6.9 | 8.1 |
| 6m | 6.9 | 8.6 | 10.4 | 12.1 |
| 8m | 9.2 | 11.5 | 13.8 | 16.1 |
| Flight type/ Speed | 4 m/s | 5 m/s | 6 m/s | 7 m/s |
| One-way | 11.5 | 14.5 | 17.5 | 20 |
| One-way | 6 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 10.1 |